We tend to have a lot of interest in the performance of DIY hardware and the level of running, but we rarely care about how they work. As a technical house, we still have to have a basic understanding of the basic working principle of the power supply, let us introduce it in a simple way.
First, why do you need power?

Power disassembly diagram
If you don't know about the power supply system, you may have a question. Why does the power supply have to pass through the power supply to make the computer hardware work properly? This has to start with the power supply workflow.

The role of the power supply is to convert the household high-voltage alternating current into pure low-voltage direct current
When the mains enters the power supply, the high-frequency clutter and the interference signal are removed by the choke coil and the capacitor filter, and then the high-voltage direct current is obtained through rectification and filtering. Then, the high-voltage direct current is converted into a high-frequency pulsating direct current through a switching circuit, and then the high-frequency switching transformer is stepped down. Finally, the high frequency AC section is filtered out, so that the relatively pure low voltage DC power for the computer is finally output.
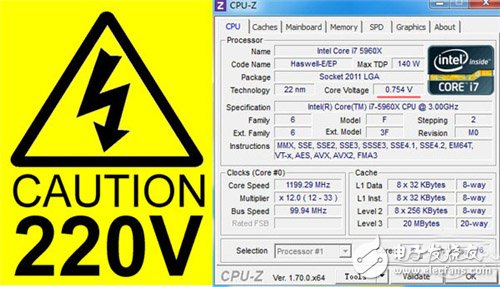
From 220V to 0.754V
Through the above simple discussion, we should know one or two. The voltage of the household circuit is 220V, and the voltage of the computer accessories we are familiar with is generally only single digit volts, such as the strongest CPU for civilian use - the standard voltage of the i7-5960X is only 1.209V. So, why can we safely disassemble the accessories when the power is on and off? That is because the entire host receives low voltage DC power after passing the power supply.
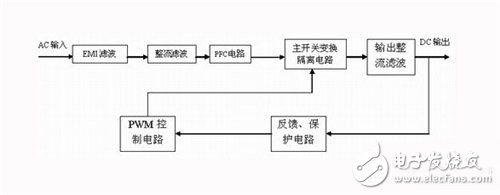
flow chart
Maybe you still can't figure it out, then a picture can tell you everything. As shown in the above figure, the general flow inside the power supply is: high-voltage commercial frequency AC input → first and second EMI filter circuit (filtering) → full-bridge circuit rectification (rectification) + large-capacity high-voltage filter capacitor (filtering) → high-voltage DC → switch Transistor → high frequency pulsating DC → switching transformer (transformation) → low voltage high frequency AC → low voltage filter circuit (rectification, filtering) → stable low voltage DC output.
Let's take a brief analysis of each link to see how 220V of power can serve individual computer accessories.
Xinxiang Mina Import & Export Co., Ltd. , https://www.mina-motor.cn
