Edge computing helps overcome challenges like load bottlenecks, latency, and fault tolerance. In the future, application systems should combine "big intelligence" in the cloud with "small intelligence" at the edge, using protocols like MQTT for data communication. Edge computing offers strong real-time performance, high stability, adaptability to various network conditions, and the ability to make autonomous decisions—making it ideal for industrial applications.
Compared to cloud services, IoT devices have unique requirements. For instance, IoT networking needs low power consumption, and devices don’t require heavy computing power. Sending all data to a central data center can slow down device response times. So, is there a more suitable local solution? The answer is edge computing.
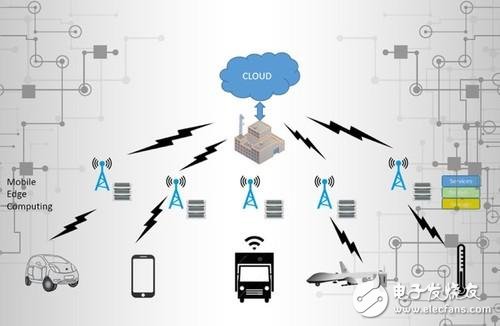
The concept of edge computing has existed for years, but it's only recently gaining traction. As more workloads move to the cloud and new technologies like the Internet of Things become widespread, demand for local processing power increases. While cloud computing excels at handling large-scale operations, its centralized approach seems outdated in the era of the Internet of Everything.
By 2020, 79% of IoT traffic will go through gateways, and over 50% of network traffic will come from IoT devices. The IoT is expected to create over 50 billion connections, adding an economic value of $1.9 trillion. Much of this data contains high-value insights, making efficient utilization a key profit driver for solution providers.
The IoT is characterized by being “small, fast, and smart.†Real-time interaction is essential, along with data preprocessing, low energy consumption, and agile connectivity. From an architectural perspective, edge computing solutions for IoT include the sensing control layer, network layer, agile controller, and application layer. The network layer enables convergence and interconnection, including edge computing for on-site processing and ensuring localized execution. This model not only provides an intelligent platform for computing, storage, and connectivity but also enhances security and reduces cloud workload.
According to Metcalfe’s Law, the value of a network grows with the square of its users. As more people and smart objects connect, the network becomes more valuable. At least 23% of IoT data holds analytical value.
In the broader evolution of edge computing, platform development and standardization are critical. Each technology has its strengths, but the real test lies in delivering tangible benefits to users. Edge computing is not just about technology—it’s about creating smarter, faster, and more responsive systems that meet the needs of today’s connected world.
Industrial Smart Module Accessories
Shenzhen Hengstar Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.angeltondal.com
