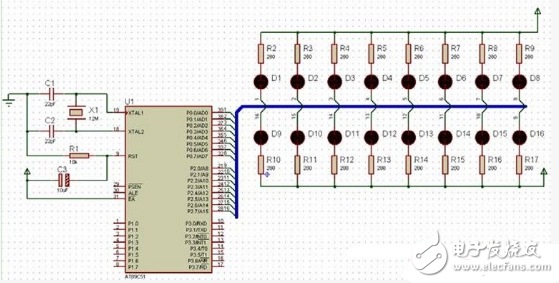
The application of LED water-flow lamps based on single-chip microcontrollers is very widespread. It's common for the core controller to be used as the main control unit, with buttons serving as input devices to realize control functions. When the number of required buttons is small, the system often uses a dedicated button. This setup allows for flexible circuit configurations and a simple software structure.
In this article, we will explore how to use TIMER0 to control an LED flow light using C programming for a single-chip microcontroller. Below is the schematic diagram illustrating the concept:
#define uchar unsigned char
#define uint unsigned int
void main()
{
uchar T_Count = 0;
P0 = 0xfe;
P2 = 0xfe;
TMOD = 0x01; // Timer 0 in mode 1
TH0 = (65536 - 40000) / 256; // 40ms timing
TL0 = (65536 - 40000) % 256;
TR0 = 1; // Start timer
while(1)
{
if(TF0 == 1)
{
TF0 = 0;
TH0 = (65536 - 40000) / 256; // Reload initial value
TL0 = (65536 - 40000) % 256;
if(++T_Count == 5)
{
P0 = _crol_(P0, 1); // Rotate left
P2 = _crol_(P2, 1);
T_Count = 0;
}
}
}
}
```
This code sets up Timer 0 to generate a 40ms delay, and after five such intervals, it rotates the bits on ports P0 and P2, creating a flowing LED effect. The program avoids using interrupts, making it simpler for beginners to understand and modify.
If you're interested in learning more about microcontroller-based LED control, you might also enjoy reading about **T0 control LED design using C language programming to achieve binary counting**.
Rubber Insulated Mining Power Cable
Rubber Insulated Mining Power Cable,Mining Cable,Mining Power Cable,Mining Power Copper Cable
HENAN QIFAN ELECTRIC CO., LTD. , https://www.hnqifancable.com
