The 2014 Nobel Prize in Physics made LEDs the focus of public concern. In recent years, from the liquid crystal display that provides backlighting to LEDs to the lamps that provide illumination, this new type of illumination is increasingly appearing in our lives. So, what are the advantages of LEDs compared to traditional lighting methods, and how does it provide us with lighting?
Incandescent: not brilliant
Before we understand how LEDs work and why they are more energy efficient, let's take a look at traditional incandescent lamps, which are commonly known as light bulbs.
If I tell you that all the objects around us are shining, you may be surprised. Yes, common sense tells us that only stars in the sky can shine, even the moon is reflected light; in addition to electric lights, candles, etc. in life, do not see other objects are also shining?
Scientists tell us that any object, as long as its temperature is higher than absolute zero, will radiate energy to the outside in the form of electromagnetic waves all the time. This is called thermal radiation. The wavelength of electromagnetic waves ranges from a few thousand kilometers to less than 1 nanometer, spanning a huge range, but only a narrow section of 400-800 nanometers can be perceived by our eyes. This is commonly known as visible light. So we can say that all objects, including ourselves, are shining.
However, an electromagnetic wave emitted by an object does not uniformly cover all wavelengths, but is mainly concentrated near a certain wavelength, and the length of this wavelength is inversely proportional to the temperature of the object. For objects with temperatures around room temperature, the electromagnetic waves they emit are mainly concentrated in infrared rays longer than visible light, so the proportion of visible light is negligible. This is why we can't see these objects shining.
As the temperature of the object rises step by step, its thermal radiation will not only become more intense, but also the electromagnetic waves emitted will gradually become visible light, so these objects that would otherwise not be illuminated will become brighter. For example, when the electric wire is heated to several hundred degrees Celsius, it will be red, because the red temperature replaces the infrared light and the heat radiation dominates. If the temperature continues to rise to a few thousand degrees Celsius, light of shorter wavelengths such as yellow, green, and blue in visible light is also released in large quantities. When the different wavelengths of visible light are mixed together, we see white light similar to sunlight, which is incandescent. Before the advent of incandescent lamps, people burned by burning firewood, lamp oil or various waxes. In fact, they are also using incandescence, but this time they use the high temperature generated by chemical reaction. The incandescent lamp uses tungsten to flow current. Heat to above 2,000 degrees Celsius to produce a large amount of visible light.
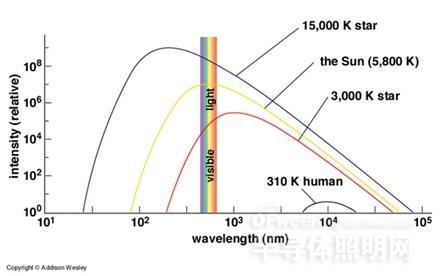
Fig.1 Comparison of thermal radiation of objects at different temperatures. From top to bottom, the temperature is 15,000K (0K corresponds to -273.15 degrees Celsius), the temperature is 5,800K (sun), and the temperature is 3,000K. The star and the human body visible at a temperature of 310K. The horizontal and vertical coordinates are the wavelength (in nanometers) and the relative intensity of thermal radiation, respectively, and the narrow color band parallel to the ordinate indicates the range of visible light. It can be seen that the temperature of the object must be high enough to emit a large amount of visible light.
100W Wall Pack Lights,Wall Pack Light Fixture,Wall Pack Light 100W,LED Wall Pack Light 140Lm/W
Vietnam JJ Lighting Company , https://www.vnjjlighting.com
